To build an Enterprise Integration Platform, there are four major categories to integrate:
- Business process layer
- Application layer
- Data layer
- Infrastructure layer
.png?width=600&name=Fig%201%2c%20%20Enterprise%20Integration%20Platform%20(2).png)
Figure 1, Enterprise Integration Platform
Most business units have multiple sub domains with their own data models, processes and technologies. Integrating all of them requires complex and efficient architecture, tools, time, and costs just to name a few.
Fortunately, you have multiple Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) tools to get the job done, though you want the ones with the end-to-end capabilities you need. Your EAI solution should also be cost-effective with a high return on your investment.

Figure 2, Point to Point Integration
However, connecting applications is not enough. You need a service oriented architecture (SOA) to make your network flexible and agile through point-to-point integration. This can lead to complex logic, redundant interfaces, scalability issues, visibility issues, and delays in your business response as your system grows. You also need a good enterprise service bus (ESB) solution to address these new concerns.

Figure 3, Message bus integration style

Figure 4, ESB
With so many open and proprietary ESB solutions available, you must choose the right tool based on your business needs, architectural capabilities, and the cost effectiveness of the solution for an enterprise integration platform.
Some of the main components of a good ESB solution include:
- Loose coupling: decoupling client and service provider.
- Protocol conversion: accept incoming protocols and communicate with different protocols to the client in the protocol it understands.
- Message Translation: transformation of messages with correct data formatting.
- Message routing: providing content based routing and itinerary services.
- Service coordination: management of business services in the correct coordination.
- Endpoint resolution: resolve any messaging issues.
- Monitoring: monitor development and run time policies, track dependencies and take care of lifecycle management.
- Adapters: adapts the protocol and formats.
- Connectors: connect with data, API, legacy mainframes and services.
- Pipes and filters: perform complex logic on a message.
- Message Bridge: how multiple messaging systems are to be connected.
- Message Bus: architecture enabling separate applications to work together in a decoupled fashion so that applications are easily added or removed without affecting others.
- Business rule engine: business process rules are defined and implemented as per the rules.
- Publish and subscribe: this is for the service.
- Transaction management: it takes care of single and multiple transactions.
- Content enricher: how to communicate with one another if the message originator lacks required data.
- Security: it has features in identity management and secured.
- Exceptional handling: it is used in fault management.
- Agility: more flexible and agile in continuous integration.
- Reusability: reuse and avoid 'reinventing the wheel'.
- Configuration: the tool has this one as the backbone.
- Load balancing: in a production environment, how services are clustered to scale up and to achieve high availability
- Connected business: entire business is connected across the enterprise.
- Integrated environment: all applications are integrated.
- Quicker time to market: advantage of using capable tool.
Referenced from Oracle - Enterprise Service Bus and HCL Technologies - Everything you need to know about Enterprise Service Bus (ESB)

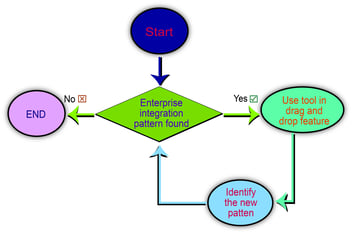
Figure 5, Flowchart
WSO2 Enterprise Integrator is an excellent open source, end-to-end ESB solution that provides your organization data integration, services integration, application integration, cloud support, and business analytics while keeping you within budget.
.png?width=600&name=Fig%206%2c%20Enterprise_Integrator%20(2).png)
Figure 6, EI
It comes as a single package with all of these modules and profiles included:
- ESB Service Integration (WSO2 ESB).
- Message broker (WSO2 MB).
- Business process (WSO2 BPS).
- Micro-services and analytics.
- Real-time data processing (WSO2 DSS).
- WSO2 Governance registry.
- WSO2 business activity monitor (BAM).
- API manager and identity server.
You will find more information on what these modules do and what the configuration options are in the reference documentation (WSO2 Library).
.png?width=600&name=Fig%207%2c%20Configuration_of_Layers%20(2).png)
Figure 7, configuration
WSO2 EAI modules makes your IT management simpler. Implementing an enterprise integration platform usually takes several different tools and about 8 months to complete, and that does not count the additional 5 months you need to develop and build the analytics system. With WSO2, you can do it in half the time and still have all the features and benefits in place when you want and need them. It also reduces your total costs and the complexity of your network.
More details are referenced in:
A new cost model for comparison of Point to Point and Enterprise Service Bus integration styles

Figure -8
Figure-8 shows how many interfaces are reduced using ESB. There are 50 applications to be integrated. It shows a maximum of 50 interfaces are needed, where as in other methods you need more than 250 interfaces.
WSO2 is listed as being one of the top tools in enterprise integration as per industry feedback.
Why should you use an ESB, such as WSO2?
The business world is undergoing a revolution. With the proliferation of technology across our lives and work, industries around the world are realising that the tried and trusted methods that have kept them moving forward might no longer suffice. Consumers today are connected, informed, and unprecedentedly technologically savvy, and as a result, the companies they deal with are expected to be the same.
Digital transformation — the process by which organizations modernize themselves to incorporate new digital technologies throughout their entire business — is becoming necessary to survive.
Modern clients want instant service and support from the brands they deal with. They want brands that make themselves available to the client in a way that suits the client, not in a way that suits the organization. And they want this experience to be offered seamlessly across every channel. In order for an organization to meet these needs and wants of the consumer, it is absolutely necessary for companies to be innovative and to stay abreast of digital updates and changes. With this in mind, decision makers in businesses are emphasizing the need for digital transformation within their organizations.
With the rise of tools such as CRM, ERP, SRP and others, it has become necessary to integrate these tools in order to have a complete view of your customers data and to provide them with the level of service they expect. Using an ESB will ensure all of your tools talk to each other and give you the power to understand your customers and drive your business forwards.
WSO2 creates a standardized, fully interoperable, single point of contact for all your business infrastructure, allowing you to quickly monitor and handle any risks and points of failure in your network. Contact us today to find out for yourself why our customers praise the effectiveness of our product at improving their IT networks and systems.



Leave a Comment